Significance, Motives and Processes Of Operations management | Inputs | Outputs
You Should Remember
There are three core stages in operations and all of them play vital role in driving efficiency and value added services in the direction of customer satisfaction. Nevertheless, the following figure demonstrates the key elements involved in Operations Management process.
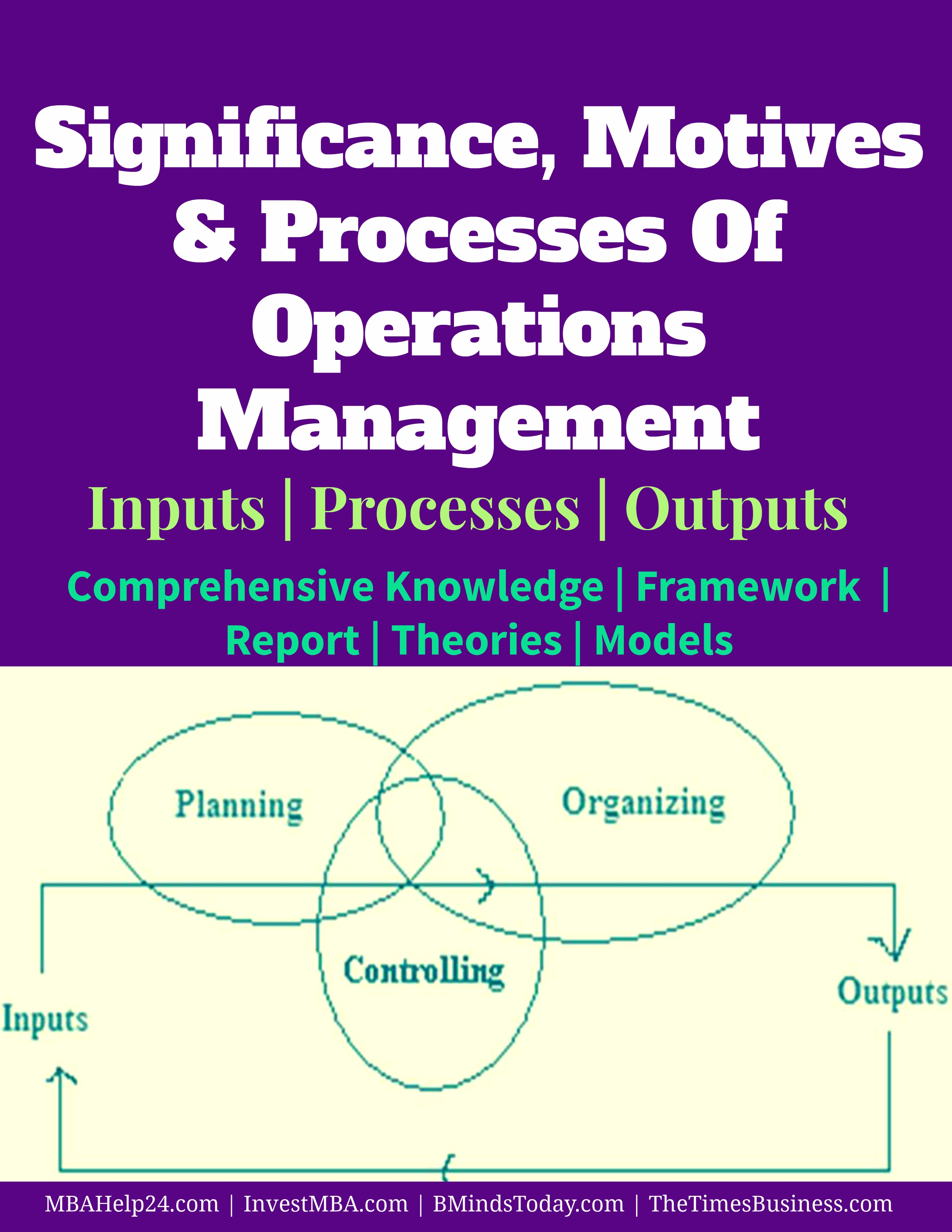
The Operations management is regarding how organisations develop or make available the products and services that accompanies the cause for their existence. Operations can be found as one of many functions (e.g. HR, marketing, finance, production) inside the organisation.
The operations function can be explained as that part of the organisation dedicated to the production or delivery of products and services. What this signifies is all organisations undertake operations activities because every single organisation produces goods and/or services.
It is a highly important task for an operations manager to monitor the processes involved and ensure all the changes to the end product are well-planned and controlled to meet the compliance.
In order to achieve strategic objectives pertaining to operational practices, it is vital to make sure that the following elements are effectively considered and efficiently met.
- Quality
- Speed
- Dependability
- Flexibility
- Cost
To experience a constant progress, the factors mentioned above should need to considered by an operations manager because they contribute to enable strategic thinking.
Significance, Motives of Operations Management
EMphasising operations in a constant manner is considered to be the most important practice to any company or organisation and there are several motives to support this.
- To improve Productivity: A measure of efficiency
The effectiveness of operations management helps to categorize the strengths and weaknesses of the end product and also enables to comprehend the transformation process. Moreover the efficient usage of Resources leads to effective outcome, in which in due course results in strengthening the financial side of the organisation.
- To meet customers competitive priorities
The operation management constantly focuses on producing effective end products or services on the basis of customer needs or market demands. These are achieved by overseeing whether operations are done with efficient usage of Resources.
Hence, the operations management plays a major role in improving the quality, productivity, accuracy, cost management, efficiency and usage of other resources for an organisation.
The Processes of Operations Management
When it comes to the process of operations management, there are three core stages which play vital role in driving efficiency and value added services in the direction of customer satisfaction. Nevertheless, the following figure demonstrates the key elements involved in operations management process.
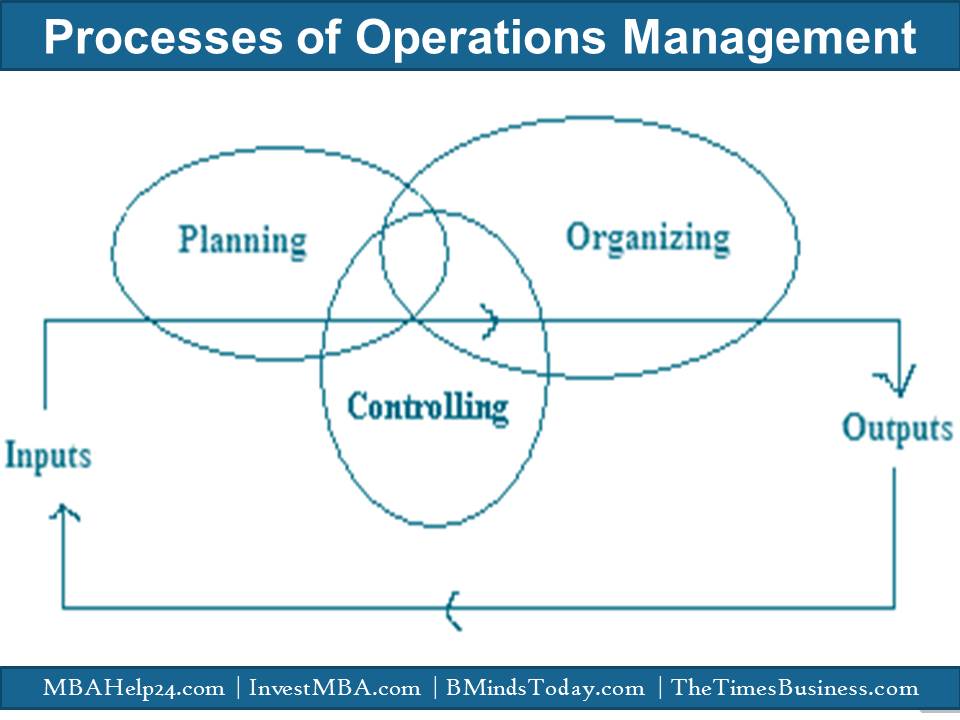
As the figure depicted, the processes of operations management are classified in three major stages; planning, controlling and organising.
In order to achieve the values and strategic objectives of an organisation, it is essential to focus on these three core stages. Notwithstanding, these core processes can be achieved by considering and implementing various significant steps such as inputs, processes and outputs.
- Inputs- it contains equipment, Labour, Infrastructure, technology, methods and other required resources.
- Processes-it entails planning, controlling and organising. This stage deals with various complexities, strategies, people expertise, implementations, monitoring and many other factors.
- Outputs- Following a successfully implementation or execution of the processes, the anticipated outcomes are attained towards quality deliverance, value added output and cost efficiency.
Concept Of Operations Management ?
supply chain Management | Comprehensive Understanding | Driven Factors Behind SCM Popularity
Strategic Decision Variables In Supply Chain Management | Inventory | transportation | Facilities
The Bullwhip Effect In Supply Chains | Causes | Countermeasures
Vendor Managed Inventory | Overview | Features | Advantages | Concerns
Linear Programming | Checklist | Structure | Model | Assumptions | Applications
Quality Management Tools | Definitions | Methods and Systems | Plan | Policy | Control | Audit
Six Sigma Project and Quality Management | DMAIC | DMADV | Structure | Phases
Kaizen Project | Benefits | Five S of Kaizen | Continuous Improvement
https://www.mbahelp24.com/processes-operations-management-significance-motives-inputs-outputs/


































































































