The diffusion practice is the method in which Innovations spread over period to other prospective buyers through communication all over a market. Diffusion study tracks the penetration and acceptance of an innovation throughout its life cycle.
Concept of Diffusion Process
The diffusion practice is the method in which innovations spread over period to other prospective buyers through communication all over a market. Diffusion study tracks the penetration and acceptance of an innovation throughout its life cycle.
Potential buyers is in many cases categorized based on how much quicker they engage in a new product. On the subject of the one particular intense, a certain amount of prospective buyers engage in the product from the moment it turns out to be available in the market. On the other hand, a certain quantity of consumers tend to be considered one of the last to invest in a brand new product or service.
Definition, Concept & Justification of marketing ?
marketing Plan: Key Elements & Action Plan
Marketing Plan: A Clear Structure/ Criteria/ Outline
‘Product Diffusion Curve’ Model
In general, the ultra-modern product adoption course of action can potentially be patterned in the shape of a bell-shaped diffusion curve the same as the following:
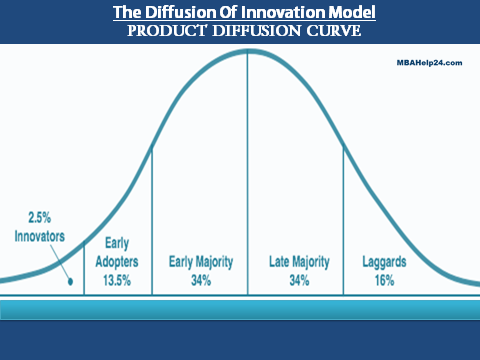
- Innovators – well prepared risk takers exactly who tend to be prepared to make an attempt to purchase an unproven product or service. Innovators represent the very first 2.5% to engage in the product.
- Early adopters – depending on the favourable reaction of innovators, early adopters subsequently start to buy the product. Early adopters are usually educated viewpoint leaders and represent about 13.5% of consumers.
- Early majority – sensible consumers who are inclined to keep away from risk, the early majority switches into the product as soon as it has been tested by the early adopters. They count on customer feedback and recommendations from others who have knowledge and experience with the product. The early majority represents 34% of consumers.
- Late majority – to some degree doubtful consumers who seem to buy a product only after it has emerged as popular. The late majority represents close to 34% of consumers.
- Laggards – consumers that try to avoid change and as a result may possibly not adopt a new right up until established choices no longer can be found in the market. Laggards represent close to 16% of consumers.
Factors that determine the rate of innovation adoption
The percentage associated with adoption is determined by several factors, such as:
- Value and continuing costs
- Observed positive aspects over substitute products
- Communicability of the product advantages
- Comfort of usage
- Promotional motivation
- Distribution strength
- Perceived potential risk
- Compatibility with present standards and principles
Whether or not a product offers high value to the customer, the organization on the other hand encounters the challenge of persuading prospective customers to try out the product and sooner or later to consider it. The product diffusion curve is to some extent responsible for the Product Life Cycle, which usually demands distinctive management strategies that depend on the product’s stage in the life cycle.
Marketing Mix: Background, Definition & Objectives of 4 P’s
The marketing Mix: 4 P’s Policy
The Life Stages Of A Product: Concept, Features, Phases & Choices
Product Life Cycle Extension Strategies
Product Diffusion Curve: Concept, Model & Determined Factors
The Diffusion of Innovation: Product Adoption Decision-Making Process & Influencing Factors
Market segmentation: Overview & Key Elements
Market Segmentation: Consumer & business Markets
Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning (STP): Definitions, Nature & Stages


































































































