Frederick Herzberg ’s Two-Factor Theory of Motivation | Motivation-Hygiene
You Should Remember
Herzberg developed the two-factor theory of motivation from an outline learned in nearly 4,000 interviews.
When questioned what “turned them on or pleased them “about their work, participants spoken primarily about elements pertaining to the nature of the work itself. Herzberg calls these “satisfier or motivation factors”.
When questioned what “turned them off or unpleased them” about their work, they spoken more about things pertaining to the work setting. Herzberg calls these “ hygiene factors ”.
Herzberg in his model suggested that the two-factor theory of motivation impacts people in various modes.
As part of understanding the attitudes and motivation of employees, Frederick Herzberg in his publication “The Motivation to Work (1959)” claimed that he executed examinations to determine which elements in an employee’s work environment triggered satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
Herzberg developed the two-factor theory of motivation from an outline learned in nearly 4,000 interviews.
When questioned what “turned them on or pleased them “about their work, participants spoken primarily about elements pertaining to the nature of the work itself. Herzberg calls these “satisfier or motivation factors”.
When questioned what “turned them off or unpleased them” about their work, they spoken more about things pertaining to the work setting. Herzberg calls these “ hygiene factors ”.
Herzberg in his model suggested that the two-factor theory of motivation impacts people in various modes.
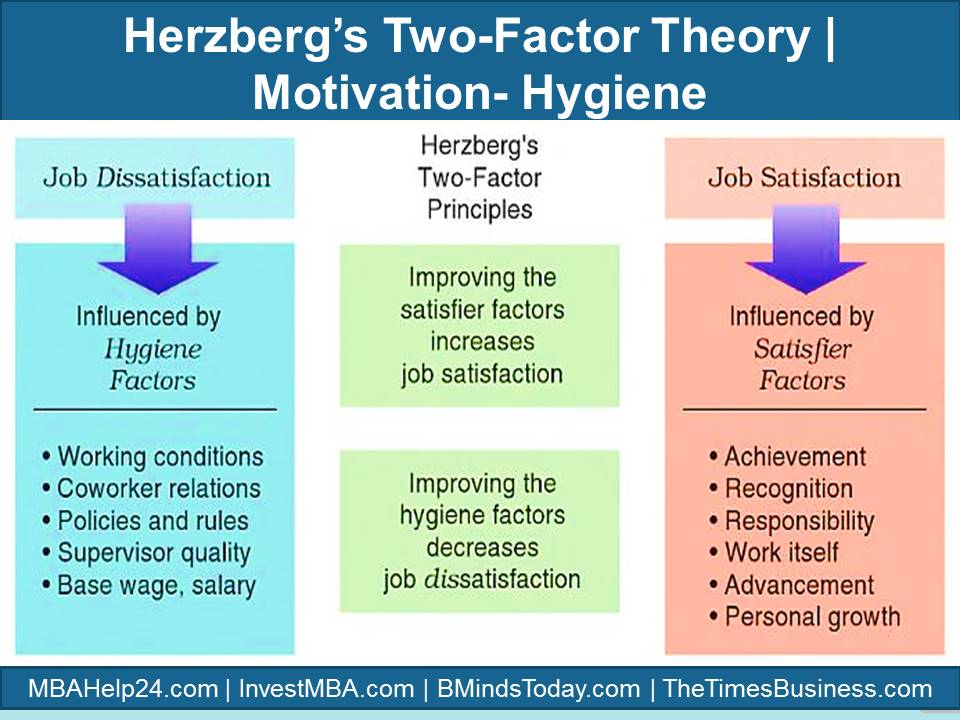
Hygiene factors
Hygiene factors are wholly connected with job dissatisfaction, in which job dissatisfaction drives up as hygiene quality goes down.
The hygiene factors such as working environments, interpersonal relations, organizational policies and administration, technical quality of supervision, and base wage or salary are discovered in the job framework.
Herzberg claims that taking adequate steps to improve hygiene factors such as implementing a non-smoking policy, adding piped-in music can only make employees less dissatisfied, but it will not help in generating high-level of job satisfaction and motivation.
Satisfier or Motivation factors
Satisfier or motivation factors, often termed motivation factors, are completely associated with job satisfaction.
They consist of a sense of achievement, feelings of recognition, a sense of responsibility, the opportunity for advancement, and feelings of personal growth.
Herzberg accept as true that the more satisfier factors there be situated in job content, the higher the motivation to work, as a result of opportunities for high-order need satisfactions.
Herzberg emphasized on adopting and implementing job enrichment techniques, in which they help to build such high content jobs.
These sorts of practices mostly make the job holder accountable for not merely undertaking the tasks, but besides planning, organizing and monitoring achievements.
Human Resource management: Definitions & Key Knowledge ?
Effective People Management | Motivation | Job Design | Reward Systems
Expectancy Theory | Essentials Of Motivation | Instrumentality | Valance
Job Design | Key Motives | Characteristics of Jobs and People | HR
Collective Approaches to Job Design | Job Enrichment | Job Rotation
Strategic Reward System | Aims | Approaches | Policies | Practices
Hierarchy Of Needs Theory | Maslow’s FIVE Needs Systems | Motivation
Impacts & Implication Of Hierarchy Of Needs Theory On HR Management
Advantages, Disadvantages & Limitations Of Maslow ’s ‘Hierarchy of Needs’ Theory
Frederick Herzberg ’s Two-Factor Theory of Motivation | Motivation-Hygiene


































































































