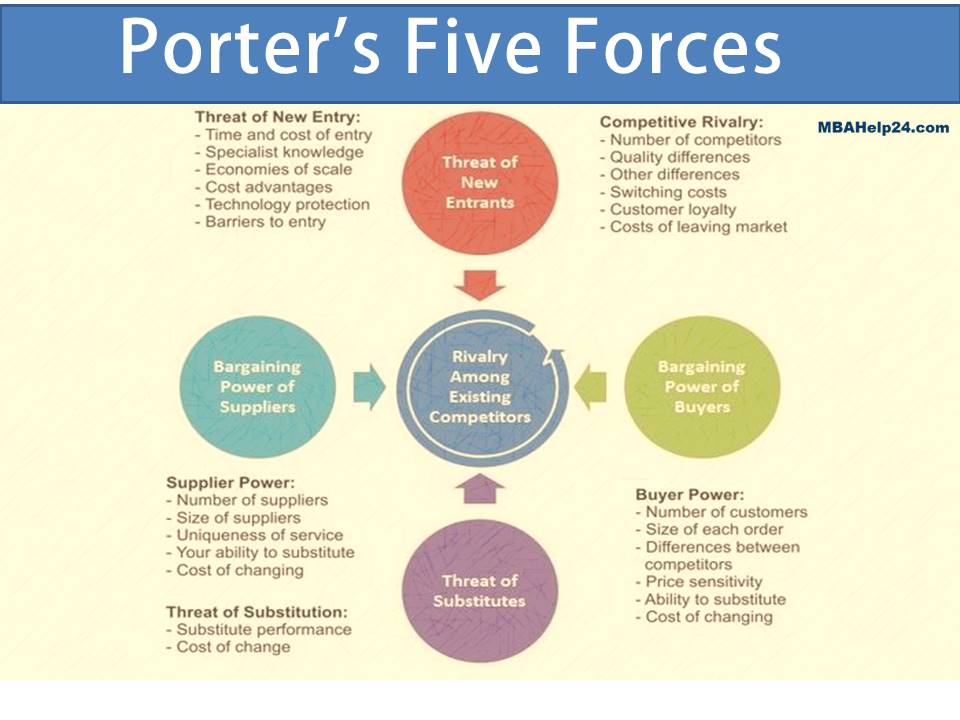
Five Forces Model focuses primarily on the various forces which in turn outline and impact the competitive environment connected with a particular industry.
On the subject of strategic viewpoint, the Five forces analysis approach is considered to be significant in order to identify the positioning of a firm in an industry, and moreover to deal with the competitiveness. It is vital to be able to discover:
- The organisation’s relationship with the similar industry players, such as;
- Customers;
- Competitors;
- Suppliers;
- Producers of substitute products or services;
- Potential new entrants;
In addition to, the five forces:
- Bargaining power of customers;
- Bargaining power of suppliers;
- Threat of substitute products and solutions;
- Threat of new entrants; and
- Intra-industry competition.
The Five Forces Model is demonstrated in the following figure:
Bargaining Power of Customers
The influence of customers in a competitive environment is determined by their capability to bargain.
This can in fact drive organizations to reduce their price ranges, call for better quality or added services, or even take edge of the competition between the different players.
For implementing this, consumers directly have the capacity to influence the revenue of the market simply because they have an impact on the costs of the product or service.
Customers possess possibly a lot more power if:
- Products and services out there are regular and differ little or no coming from competitors;
- At this time there are only a small number of customers or clients or perhaps they buy huge amounts;
- The transport or transform costs from one supplier or service provider to another are modest;
- They are able to directly incorporate the supplier’s activities into their own production chain.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Suppliers can have an impact on the profitability of a firm through process of imposing their very own terms and conditions (when it comes to cost or quality) in the same manner as the customers.
The power of suppliers is substantial in cases where:
- They have a great number of customers or clients from various markets or industries;
- They are in particular focused or in a monopoly scenario;
- The transfer cost is extremely high;
- They supply differentiated products and solutions and there are virtually no substitute products and solutions for what they give;
- They are in a position to integrate more activities into their primary business venture further along the supply chain.
Suppliers or service providers have a strong command over an industry by re-negotiating the terms and conditions of an agreement involving themselves and their clients in addition to through continuously attempting to find the most beneficial .
Strategy’s Three Key Challenges ?
Beyond Formulation: Results-oriented strategy leadership?
Strategic Planning: Overview, Significance & Outcomes
The Strategic Planning Process: A Fundamental View
Vision, Mission, Value & Objective Statements: What & What Not?
Threat of Substitute Products
Substitute products and solutions provide alternate options to the active offer in an industry. They react to very similar needs in some sort of unique or even very creative manner.
The present time when it comes to every Single Marketplace, substitute products and solutions turn out to be serious threats in cases where:
- The price of the substitute product or service is cheaper;
- They provide an improved top rated quality;
- The cost of transferring to the substitute product or service is low.
In many instances, substitute products and solutions create a potential threat simply by acquiring and maintaining share of the market and in addition keeping pressure level on the prices.
Threat of New Entrants
Cutting edge entrants possess a capability to be able to shake up the industry via offering better value to consumers.
Their unique passion to attain fresh market share enhances the amount of pressure on price ranges as well as plans and policies concerned with financial impact.
The threat of new entrants happens to be more powerful when:
- There is no patent to be able to safeguard technological Innovation, which makes it possible for quick access to them;
- Limitations to entry and also the funds prerequisites have become affordable.
Rivalry among Existing Companies Or Intra-Industry Competition
The level of competition present in an industry is based on the industry’s focus, product or service differentiation, operating leverage in cost framework, being able to deal with capacity flexibly and moreover distinct possibilities to attain competitive edge.
If competition among companies in an industry is low, the industry is regarded to be disciplined. This specific discipline can potentially effect from the industry’s track record of competition, the position of leading company, and / or perhaps informal compliance with a generally speaking comprehended Code of Conduct.
The power of rivalry is influenced by the following industry traits:
- An increased number of companies will increase competition simply because a lot more companies need to compete for the same target market as well as resources.
- Sluggish market growth provokes companies to battle for share of the market.
- Increased storage space running costs trigger a manufacturer to sell products and solutions at the earliest opportunity.
- Low-level of product or service differentiation is involved with greater degrees of rivalry.
- A diversity of rivals with various cultures, backgrounds, and also beliefs cause an industry shaky.
PESTLE Analysis of the Macro-environment: Definition & Purpose
PESTLE Analysis: 6 Core Variables
SWOT Analysis: Definition & Primary Advantages
SWOT Analysis Framework: Internal & External Scan
Competitive Advantage: Cost Advantage & Differentiation


































































































